Direct Database Access¶
If you have to make changes to your ThinkUp database manually, you can do so from the command line, or using an interface like phpMyAdmin.
Access ThinkUp’s MySQL database via phpMyAdmin¶
Many web hosts offer access to your MySQL databases via phpMyAdmin. If you have phpMyAdmin installed, here’s how to access your ThinkUp database using it.
- Log in to phpMyAdmin with your username and password for your account.
- Click on the thinkup database in the left hand column - whatever you named it during installation.
- From here you can choose any table to view and update its contents.
Access ThinkUp’s MySQL database via the Command Line¶
You will need your ThinkUp database user name and password, which you set when you installed ThinkUp.
Log in to your database at the command line. (Notice there should be no space between -p and your password.)
mysql -u <database owner> -p<password> ***** Output ******************************** Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MySQL connection id is 135 Server version: 5.1.41-3ubuntu12.10 (Ubuntu) Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement. *********************************************
Change to your ThinkUp database.:
mysql> use <database name you created or the thinkup install created for you>
Hint: if you don’t know the name then type this at the command line:
mysql> show databases;If your database name is ‘thinkup’, enter:
mysql> use thinkup; ***** Output ******************************** Reading table information for completion of table and column names You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A Database changed *********************************************
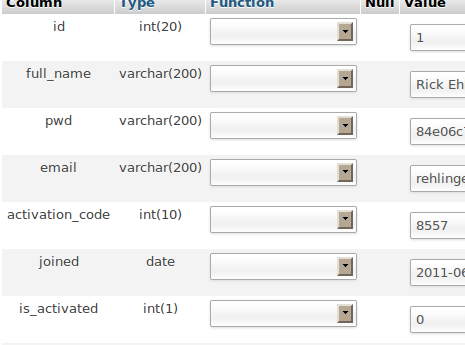
From here you can view the contents of tables using SELECT and update them using UPDATE. For example, to check the value of the is_activated column in the owners table, use this command.
mysql> select id,full_name, is_activated from tu_owners; +----+---------------+--------------+ | id | full_name | is_activated | +----+---------------+--------------+ | 1 | Rick Ehlinger | 0 | +----+---------------+--------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
To change the value of the is_activated column to 1, use this command.
mysql> update tu_owners set is_activated=1 where id=<the id of the person you are activating>; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0 mysql> commit; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
When you’re done making your changes, exit to the command prompt.
mysql> exit